An Electromagnetic Wave Consists Of
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic (EM) spectrum is the range of all types of EM radiation. Radiation is free energy that travels and spreads out as it goes – the visible lite that comes from a lamp in your firm and the radio waves that come from a radio station are two types of electromagnetic radiation. The other types of EM radiation that make up the electromagnetic spectrum are microwaves, infrared low-cal, ultraviolet light, X-rays and gamma-rays.
You know more about the electromagnetic spectrum than you may recollect. The image beneath shows where you lot might encounter each portion of the EM spectrum in your twenty-four hour period-to-day life.
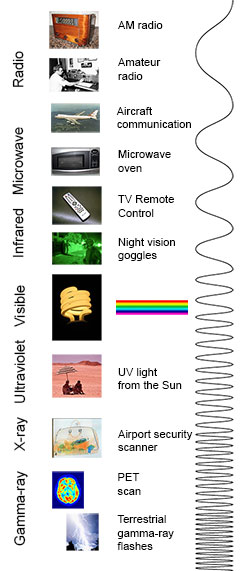
The electromagnetic spectrum from lowest energy/longest wavelength (at the top) to highest energy/shortest wavelength (at the bottom). (Credit: NASA'due south Imagine the Universe)
Radio: Your radio captures radio waves emitted by radio stations, bringing your favorite tunes. Radio waves are likewise emitted by stars and gases in space.
Microwave: Microwave radiations volition cook your popcorn in only a few minutes, just is likewise used by astronomers to learn about the structure of nearby galaxies.
Infrared: Night vision goggles choice up the infrared light emitted by our skin and objects with oestrus. In space, infrared light helps the states map the dust between stars.
Visible: Our eyes detect visible calorie-free. Fireflies, low-cal bulbs, and stars all emit visible light.
Ultraviolet: Ultraviolet radiations is emitted past the Sun and are the reason skin tans and burns. "Hot" objects in infinite emit UV radiation besides.
10-ray: A dentist uses Ten-rays to image your teeth, and airport security uses them to see through your bag. Hot gases in the Universe as well emit X-rays.
Gamma ray: Doctors utilize gamma-ray imaging to see inside your body. The biggest gamma-ray generator of all is the Universe.
Is a radio moving ridge the aforementioned equally a gamma ray?
Are radio waves completely different concrete objects than gamma-rays? They are produced in different processes and are detected in unlike ways, simply they are not fundamentally unlike. Radio waves, gamma-rays, visible light, and all the other parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are electromagnetic radiations.
Electromagnetic radiation tin be described in terms of a stream of mass-less particles, chosen photons, each traveling in a wave-like pattern at the speed of light. Each photon contains a certain amount of energy. The different types of radiation are divers by the the amount of energy found in the photons. Radio waves have photons with low energies, microwave photons have a fiddling more energy than radio waves, infrared photons have however more, then visible, ultraviolet, 10-rays, and, the about energetic of all, gamma-rays.
Measuring electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation tin be expressed in terms of energy, wavelength, or frequency. Frequency is measured in cycles per second, or Hertz. Wavelength is measured in meters. Energy is measured in electron volts. Each of these three quantities for describing EM radiation are related to each other in a precise mathematical way. Only why have three means of describing things, each with a different set of physical units?
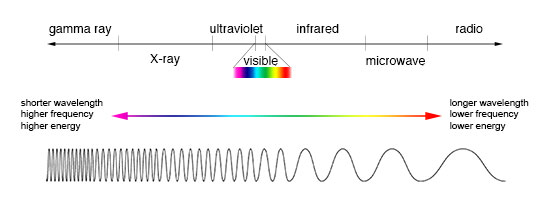
Comparison of wavelength, frequency and energy for the electromagnetic spectrum. (Credit: NASA'southward Imagine the Universe)
The short answer is that scientists don't like to use numbers whatever bigger or smaller than they take to. It is much easier to say or write "two kilometers" than "two thousand meters." Generally, scientists utilise whatsoever units are easiest for the type of EM radiation they work with.
Astronomers who study radio waves tend to use wavelengths or frequencies. Most of the radio function of the EM spectrum falls in the range from nearly 1 cm to 1 km, which is 30 gigahertz (GHz) to 300 kilohertz (kHz) in frequencies. The radio is a very broad part of the EM spectrum.
Infrared and optical astronomers generally utilise wavelength. Infrared astronomers utilize microns (millionths of a meter) for wavelengths, so their role of the EM spectrum falls in the range of 1 to 100 microns. Optical astronomers use both angstroms (0.00000001 cm, or
The wavelengths of ultraviolet, 10-ray, and gamma-ray regions of the EM spectrum are very minor. Instead of using wavelengths, astronomers that written report these portions of the EM spectrum ordinarily refer to these photons by their energies, measured in electron volts (eV). Ultraviolet radiation falls in the range from a few electron volts to about 100 eV. Ten-ray photons have energies in the range 100 eV to 100,000 eV (or 100 keV). Gamma-rays then are all the photons with energies greater than 100 keV.
![]() Bear witness me a chart of the wavelength, frequency, and free energy regimes of the spectrum
Bear witness me a chart of the wavelength, frequency, and free energy regimes of the spectrum
Why exercise nosotros put telescopes in orbit?
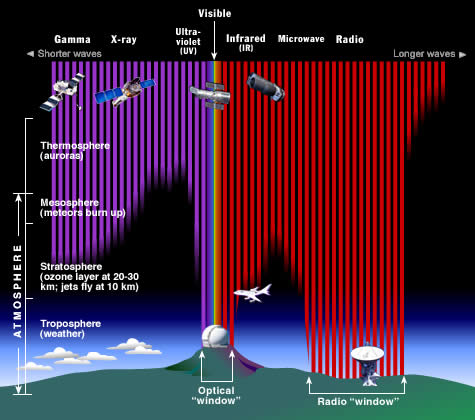
The Earth's atmosphere stops most types of electromagnetic radiations from infinite from reaching Earth's surface. This illustration shows how far into the atmosphere dissimilar parts of the EM spectrum can get before being absorbed. Only portions of radio and visible light accomplish the surface. (Credit: STScI/JHU/NASA)
Most electromagnetic radiation from space is unable to reach the surface of the Globe. Radio frequencies, visible light and some ultraviolet light makes information technology to ocean level. Astronomers tin observe some infrared wavelengths by putting telescopes on mount tops. Airship experiments can reach 35 km to a higher place the surface and can operate for months. Rocket flights can have instruments all the style in a higher place the Earth'southward atmosphere, but only for a few minutes before they autumn dorsum to Earth.
For long-term observations, however, it is all-time to take your detector on an orbiting satellite and become above information technology all!
Updated: March 2013
An Electromagnetic Wave Consists Of,
Source: https://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/science/toolbox/emspectrum1.html
Posted by: urestiboure1963.blogspot.com


0 Response to "An Electromagnetic Wave Consists Of"
Post a Comment